Understanding the Differences in Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy has become an essential non-invasive treatment in modern rehabilitation, orthopedics, and sports medicine. As the clinical use of shockwave machines continues to expand worldwide, one common source of confusion remains: the difference between focused shockwave therapy and radial shockwave therapy.
Although both fall under the umbrella of shockwave therapy, these two technologies differ significantly in physical principles, energy distribution, and clinical application. Understanding these differences is critical for medical professionals, therapists, and clinics aiming to apply shockwave therapy more effectively.
Why It Is Important to Distinguish Between Focused and Radial Shockwaves
The term shockwave is often used broadly in clinical marketing, yet not all shockwave therapies operate in the same way. Differences in wave generation and propagation directly influence how energy interacts with biological tissue.
As a result, the therapeutic outcomes of shockwave therapy are closely linked to the underlying technology of the shockwave machine being used.
What Defines a “True” Shockwave?
From a physics standpoint, a shockwave is characterized by:
- An extremely rapid rise in pressure
- A high peak pressure followed by a short negative phase
- Non-linear propagation through tissue
These characteristics distinguish shockwaves from conventional ultrasound or vibration-based therapies. In clinical practice, focused shockwave therapy most closely aligns with this classical physical definition, while radial shockwave therapy represents a different form of acoustic pressure transmission.
Focused Shockwave Therapy: Principle and Energy Distribution
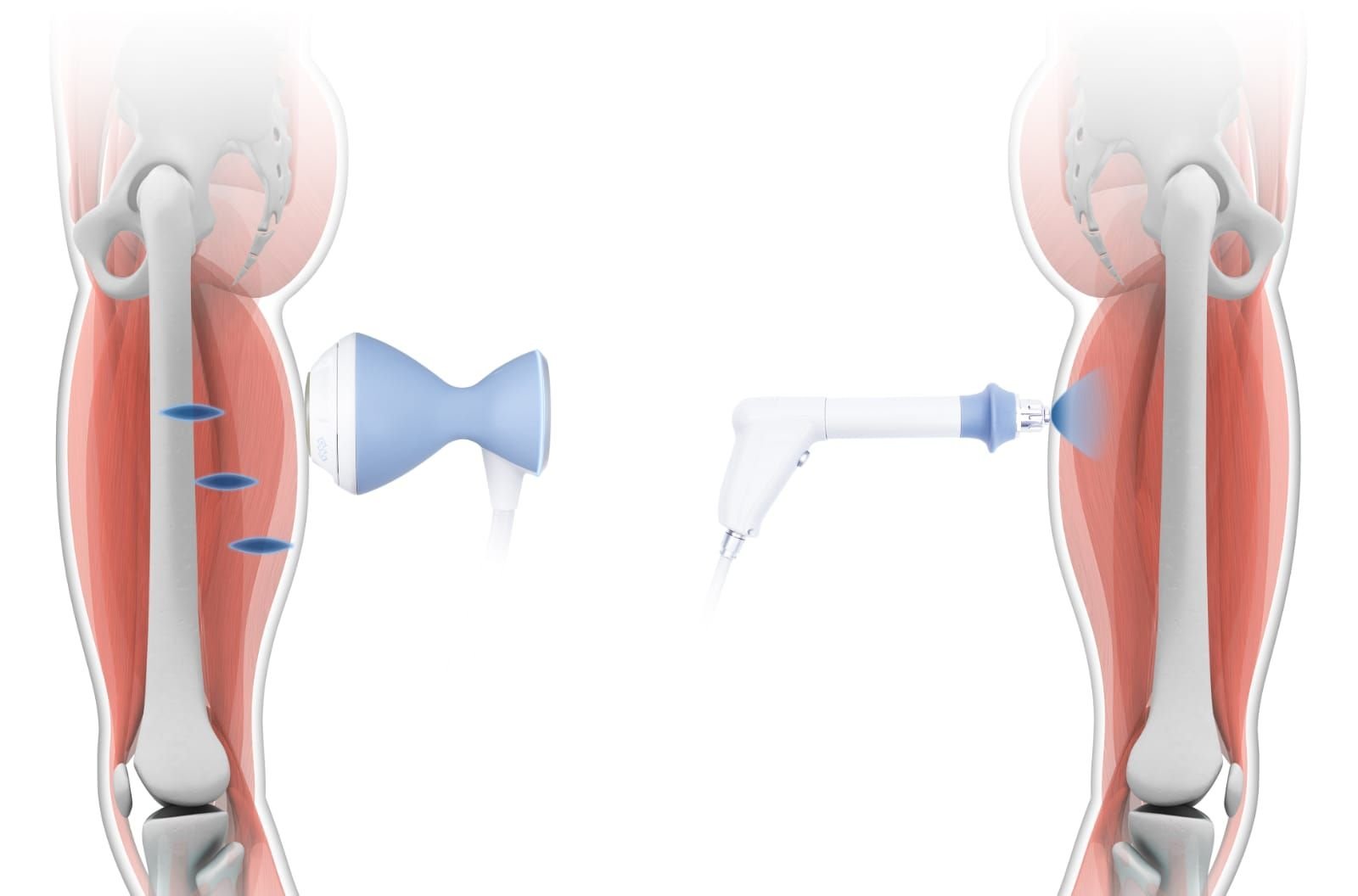
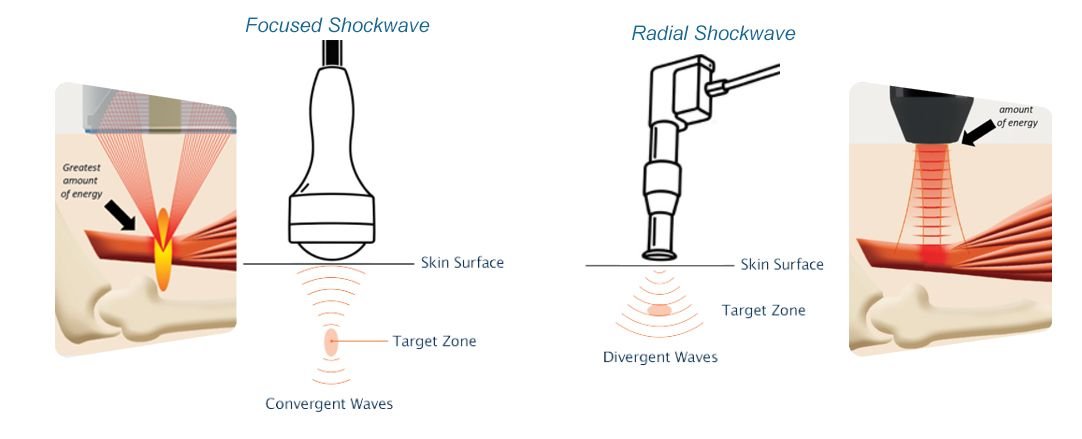
Focused shockwave therapy generates high-energy acoustic waves that converge at a specific focal point within the body. This focal zone can be positioned at varying depths, allowing energy to be delivered precisely to deep pathological tissue while minimizing surface dispersion.
Key characteristics of focused shockwave therapy include:
- Clearly defined focal depth
- High energy flux density at the target zone
- Concentrated mechanical stimulation
Because the peak energy is released beneath the skin surface, focused shockwave therapy is commonly associated with deep tissue interaction and targeted biological responses.
Radial Shockwave Therapy: Principle and Energy Distribution
Radial shockwave therapy, also known as radial pressure wave therapy, produces acoustic waves that propagate outward from the applicator surface. The highest energy is generated at the skin level and gradually dissipates as the wave travels deeper into the tissue.
Key characteristics of radial shockwave therapy include:
- Maximum energy at the applicator surface
- Gradual energy attenuation with depth
- Broad treatment area rather than a single focal point
This radial dispersion pattern makes radial shockwave therapy suitable for addressing superficial and wide-area soft tissue conditions.
Penetration Depth and Tissue Interaction
One of the most fundamental differences between focused and radial shockwave therapy lies in how deeply energy penetrates the tissue.
- Focused shockwave therapy allows energy to concentrate at depths that may reach 10–12 cm, depending on system configuration and treatment parameters.
- Radial shockwave therapy typically affects tissues within a more superficial range, often between 3–7 cm.
This distinction explains why different shockwave techniques are selected for different clinical objectives. Tissue depth, density, and pathological characteristics all influence which energy delivery model is most appropriate.
Clinical Application Considerations
While both approaches are widely used in shockwave therapy, their clinical focus often differs:
Focused shockwave therapy is commonly applied in cases involving:
- Deep-seated tendinopathies
- Chronic calcified lesions
- Bone-related pathologies and delayed healing
- Long-standing musculoskeletal disorders
Radial shockwave therapy is commonly applied in cases involving:
- Myofascial pain and muscle tension
- Superficial soft tissue disorders
- Functional rehabilitation and muscle recovery
- Large-area treatment protocols
It is important to note that these applications reflect general clinical practice patterns rather than strict limitations.
Treatment Experience and Operational Characteristics
From an operational perspective, focused and radial shockwave therapies also differ in how treatments are delivered:
- Focused shockwave therapy typically emphasizes precision, targeting specific anatomical structures with controlled energy delivery.
- Radial shockwave therapy often involves broader, sweeping treatment techniques that address larger tissue regions.
These differences influence treatment workflow, practitioner technique, and patient experience, further reinforcing the importance of selecting the appropriate shockwave technology.
The Trend Toward Multi-Technology Shockwave Systems
Modern shockwave therapy increasingly recognizes that no single technology addresses all therapeutic needs. As a result, many advanced shockwave machines now integrate both focused and radial shockwave capabilities.
This multi-technology approach allows clinicians to adapt treatment strategies based on:
- Tissue depth
- Condition chronicity
- Treatment goals
Rather than viewing focused and radial shockwave therapies as competing methods, contemporary practice often considers them complementary components of a comprehensive shockwave therapy platform.
Focused shockwave therapy and radial shockwave therapy represent two distinct approaches within the broader field of shockwave therapy. Their differences are rooted in fundamental physical principles, energy distribution patterns, and tissue interaction mechanisms.
By understanding how each type of shockwave functions, clinicians and therapy providers can make more informed decisions when selecting and applying a shockwave machine. Ultimately, effective shockwave therapy begins not with technology preference, but with a clear understanding of how acoustic energy interacts with the human body.